
Косметика.
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY OF WOOD
Profile of the Department:
nanobiotechnology
Cosmetics - care for the outer covering (skin, teeth, hair).
Perfume - means to give a pleasant scent around the person.
Nose around 1500 people distinguish odors.
Key odors:
1. Flower
2. Mint
3. ethereal
4. camphoric
5. musky
6. sharp
7. putrefactive
The surface of the skin in the adult of about 2 m2. Condition of the skin depends on age, nutrition and lifestyle. In adult human skin contains 60% moisture, 90% of children. In 1 cm2 of skin is about 100 long and 200 nerve endings (receptors). Weight of skin about 5% by weight of man. The average life changes 18 kg of skin.
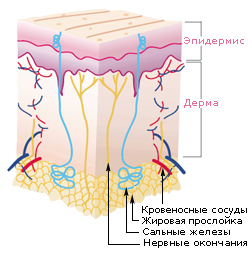
Layers of the skin:
1. external - the epidermis
2. Medium - dermis
3. internal - hypodermis
Epidermis.
The epidermis is formed by several tens of layers of cells. The outer layer - horn, which consists of old and dead cells. The dead cells are replaced by younger at different speeds. For example, a complete upgrade of the epidermis on the soles - 1 month, at the elbow -10 days. On the surface of the skin is the hydro-lipid mantle in the form of a thin film having an acidic environment. It does not allow pathogens to enter through the skin disease. This mantle is composed of fat, sweat and viscous substances, which bind the individual horny cells. In the deepest layer of the epidermis are melanocytes (cells that produce melanin - the coloring matter, which depends on the color of the skin). Increased formation of melanin by UV rays, it is the cause of sunburn.
Active
In the upper part of the gland is located under the epidermis, which together with the sweat glands nourish the hydro-lipid mantle. Below lie layers of elastic fibers that give elasticity, and collagen fibers that give strength.
Hypodermis
Options hypoderm - insulation and mitigation of mechanical effects on internal organs. Subcutaneous adipose tissue in different parts of the body has a different thickness. Best of all it is developed on the abdomen, buttocks and hands. Very little - in the auricles and lips. In the subcutaneous fat deposited reserves of fat that are consumed with illness and adversity. Fiber protects from bruises and hypothermia.
Epidermis with derma binds the basement membrane. It consists of a single row of cells that continually divide and provide the updated skin. In addition, the membrane is a filter that does not permit large charged molecules. Epidermis through the membrane can affect the dermis, causing the increase or slow down the synthesis of various substances.
The main cells of the epidermis are keratinocytes. They are born, evolve and die. Tearing himself away from the basement membrane, they take the path of inevitable destruction, and gradually moving to the surface of the skin and turn into dead cells - karneotsit.
The dermis is composed of protein collagen (70 ... 80%), elastin (1 ... 3%) and proteoglyukanov. Collagen gives the elasticity of the dermis, elastin - elasticity, proteoglyukany retain water. The most important skin cells - fibroblasts, which is the synthesis of collagen, elastin and proteoglyukanov.
Skin vessels
Of the blood vessels in the dermis receives moisture and nutrients. Moisture trapped hygroscopic molecules of proteins, which in this transition in gel form. Part of the moisture rises above penetrates the epidermis and then evaporates from the surface.
In the epidermis of the blood vessels there. Moisture and nutrients are slowly seep into the epidermis from the dermis. By reducing the intensity of blood flow in the vessels of the dermis in the first to suffer the epidermis.
Functions of the skin
Protective
Mechanical protection of the skin from external factors provided by compact horny layer of the epidermis, the skin's elasticity, its elasticity and shock-absorbing properties of the subcutaneous tissue. Due to this, the skin resists mechanical shocks - shocks, stretching, etc. Leather, mainly protects the body from radiation exposure. IR - rays almost entirely retained horny layer of the epidermis. UV - rays are delayed skin part. Penetrating the skin, UV - rays stimulate the production of protective pigment melanin, absorbs these rays.
The skin protects the body from the penetration of chemicals, including aggressive. Protection against microorganisms is provided bactericidal properties of skin. On the surface of healthy human skin is from 100 thousand to 30 million micro-organisms (bacteria) per square centimeter. Healthy skin is impermeable to microorganisms. They are removed together with horny scales, fat and sweat. In addition, sebum and sweat on the skin surface creates an acidic environment that is unfavorable for the reproduction and contributes to rapid loss of many microorganisms. Bactericidal properties of the skin is reduced by pollution, hypothermia and some diseases. If microbes penetrate the skin, in response to this there is a protective inflammatory response of the skin. The skin is part of the human immune system.
Electrical
The skin has a low electrical conductivity, because horny layer of the epidermis bad conducts electrical current.
Wet skin conduct current better than dry. In a sleeping man skin resistance is three times higher than that of waking. In a state of nervous excitement conductivity increases. Skin is more resistant to currents of high frequency than low frequency currents and DC.
Leather women's better to talk than the skin of men. One day human skin at a temperature of about 300? Provides 8 grams of carbon dioxide and consumes 4 g of oxygen, which is 2% of total gas exchange of man. Dermal respiration increases with increasing air temperature during exercise, during digestion, increasing the atmospheric pressure and in inflammatory processes in the skin.
Absorption
The absorption of water and salts dissolved in it through the skin occurs.
Fat-soluble substances are absorbed through the epidermis. Easily absorbed by the gases and solvents, fats (chloroform, diethyl ether, etc.). Most toxic gases can not penetrate through the skin, except for special agents. Medications absorbed through the skin in different ways. For example, morphine - easily, antibiotics - bad. Suction capacity of the skin increased after loosening of the horny layer of the epidermis warm baths and compresses. For lubrication of the skin fat absorptivity increases.
Secretory
At the expense of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Number allocated through these substances depends on the age, nature of food and some environmental factors. In some diseases of the kidneys, liver and lungs, the discharge of substances that are normally removed by kidneys (acetone, bile pigments), are removed through the skin. Sweating is under the control of the nervous system. Average per night sweat glands isolated from 0,7 to 1,3 liters of sweat. The intensity of sweating depends on the ambient temperature and general condition of the body. Sweating increases at high temperature and physical activity, decreases during sleep and rest. Sweaty fat in the glands of 2 / 3 consists of water, and 1 / 3 of the analogues casein (bone glue), cholesterol and salt. With sebum bold and related organic acids and metabolic products of sex hormones. Maximum activity of the sebaceous glands of the skin begins with puberty and 25 years, and then the activity of the glands is reduced.
Thermostatic
During the life of the body produces heat. However, he is obliged to maintain a constant body temperature, necessary for normal functioning of the internal organs, and it should not depend on the fluctuations of external temperature. The process of maintaining a constant temperature - thermoregulation. 80% of it is carried out through the skin by radiation, heat conduction and evaporation of sweat. The layer of subcutaneous fat and grease of the skin are poor conductors of heat, therefore, hinder the flow of excessive cold or heat from the outside, as well as excessive heat loss. Insulating function of skin is reduced by its moisture. When the ambient temperature is vasodilatation skin and sweating, due to the evaporation of perspiration increases heat the skin to the environment. By lowering the temperature of the environment reflex constriction of blood vessels of the skin, the activity of sweat glands is suppressed and heat transfer is reduced. In the thermoregulation of the skin are involved the nervous system and hormones of the endocrine glands. The temperature of the skin depends on time of day, nutritional status, age and other factors. The temperature of the skin at different sites varies and ranges from 31 to 37 ° C.
In metabolic processes (metabolism)
In the skin there is an exchange of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, salt and water metabolism. The intensity of water, salt and carbon dioxide exchange skin slightly inferior to the liver and muscles. Compared with other organs of the skin intensively accumulate and gives and water (two times more than the lungs). Subcutaneous cellular tissue (hypodermis) is a storehouse of nutrients that the body expends during periods of undernutrition.
Vascular
Cortex affects the tone of the vascular network of the skin. Tonus - width of the lumen and the rate of blood flow. Some emotion (anger) reinforce the tone, while others (fear) decrease. Blood vessels respond quickly to pain, temperature change, mechanical and chemical irritation. The intensity of the vessels depends on the age and characteristics of the human nervous system. In the case of expansion of all blood vessels of the skin can accommodate up to 1 liter of blood. The rapid expansion of blood vessels, such as heat stroke, can cause serious blood disorder.
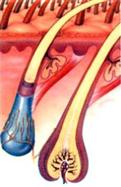
The inner medulla is the center of the hair. In very thin hair, it is not.
The middle layer contains granules of color pigments. Hair color depends on the number, size and distribution of granules in the middle layer. The cuticle has a porous surface, least of all in the roots of her hair. Dry hair is more porous than fat. Effect of hair dyes and lightening shampoos based on penetration into the cuticle and the interaction with the pigments of the middle layer.
Cuticle can be damaged from the following reasons:
1. Effects of the Sun
2. too frequent combing or washing hair
3. excessive use of hair dryers (especially for dry hair)
4. too often paint or lighting
5. perm
6. effect of chlorinated water
Under the influence of these factors, the upper layer of cells begin to stratify and fall off, hair tangles easily, lose their luster and strength, the tips of hair whipped.
If the damage the hair shaft hair dying, because the hair shaft is not restored.
Hair is divided into 3 categories and 4 types.
Categories of hair: medium, thin, thick.
Types of hair: dry, normal, mixed.
The hair on the head are unevenly. They were more on the crown, less on the temples and at the forehead.
Fastest growing hair on his head (for 3 days - 1 mm), the slowest - at the eyebrows. Separate hair grows from a few months to 6 years. Eyelash live up to 5 months, Pushkova hair - up to 10 months.
If a day a person falls from 30 to 50 hair - this is normal. The average growth of hair in a healthy person is 10 cm per year. The most intensive growth in age from 15 to 30 years, after 50 years of growth is slowing sharply. Hair grows faster in summer than in winter.
Women's hair will grow faster than males and less likely to drop out. Hair of eyebrows and eyelashes completely refreshed every 5 months.
Healthy hair is usually strong and resilient. Hair can be stretched to 1 / 5 of its length and then it returns to its previous state. For strength, they are comparable to aluminum and in some cases, a load of 200g.
Trichotrophy
Thick and beautiful hair grow with a balanced diet. Excess fat and sugar in the diet leads to obesity, diabetes and hair loss. Lack of Zn, S, Fe - to dryness, thinning and hair loss.
Vitamins are involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, metabolic processes and the construction of the hair.
The most important hair vitamins:
Vitamin A: meat, fish, cheese, carrots.
Vitamin D: eggs, liver.
Vitamin E: Sunflower seeds, nuts.
Vitamin C: Fresh fruit.
Minerals. Lack of Fe and Zn leads to hair loss. Too much coffee or tea reduces the absorbability of iron and actively removes it from the body.
Proteins. The hair on 65% consist of protein. The main consumption of protein intake must occur in the first half of the day, but not for dinner. Protein foods in order anticholesterol arranged in series:
Fish - bird - cereals - nuts - seeds - meat (especially beef).
To strengthen the hair and joints need gelatin and carbohydrates. In the daily diet carbohydrates should be at least 2 / 3. The best honey than sugar.
Fat. Animal fats contain a lot of cholesterol. A certain amount of cholesterol people should consume, because without skin and hair will not have a healthy appearance. Better, if possible, replace animal fats with vegetable, which should not be less than half of all fats. Fatty fish better than fatty meat.
Functions of hair:
1. hair protects the head in case of overheating and overcooling
2. Pushkova hair participate in touch
3. eyelashes protect the eyes
4. hair in nose and ears delay dust
Hair are of 3 types:
1. long (very strong)
2. bristly - eyebrows, eyelashes, nose and ears
3. Pushkova - on the skin of the face, trunk and extremities
Part of the hair, which is located above the skin, called the pivot, and hidden in the skin - the root. The root ends in extension, which is called the hair bulb. Because it is a growth of hair.
In the structure of hair distinguish 3 layers:
1. inner medulla
2. middle cortical layer
3. scaly outer layer (cuticle)
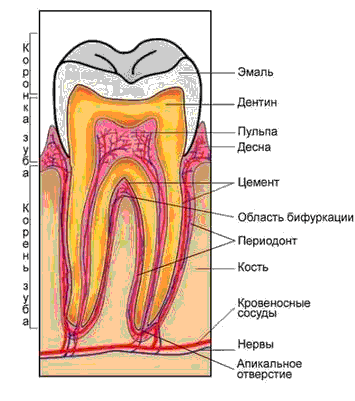
Functions of teeth
The man is 28 to 32 teeth. The main functions of teeth:
- Food
- Formation of sounds.
Development of teeth lasts up to 20 years and is divided into 3 periods:
First period - from birth to 7 months. The first milk tooth appears at 6-7 months.
Second period - from 7 months to 7 years. During this time, grow all 20 primary teeth. Complete formation dentitions ends at 2 ... 3 years.
Third period - from the end of 6-year to 13 years. Baby teeth are in constant change. The first permanent tricuspid erupt at age 6 ... 7 years.
The most common dental disease - tooth decay.
Caries - a process in which there is softening of the hard tissue of teeth, leading to the formation of cavities. The reason - the germs.
Bacteria digesting food residue to form a soft plaque, which adheres to the tooth surface. Over time, dental plaque is formed of several layers of microorganisms. They convert sugar into acids that enamel demineralization and destroy it.



